



The Europe has safety certification requirements formotor vehicle, components and systems that associated with security, and expressed as mark E and mark e.
The E-mark that approved by ECE derives from the regulations issued by Economic Commission of Europe. Recently ECE includes more than 50 countries, it also includesEastern Europe,Southern Europe such non-European countries apart from EU members, ECE regulation is recommended to the members but not mandatory standard. From the point of market demand, the ECE members usually willing to accept the test reports and certificates that comply with ECE regulations. The involved products are components and system units, but no the whole vehicle approval regulations.
The domestic common E mark certification products include tyre,safety glass,auto bulb, warning triangle, vehicle electronic products, etc. The testing organizations that perform E mark certification are usually the technical service organizations of ECE members, the license issuing agencies that issue E mark certification are government departments of ECE members. Different countries have their respective numbers:
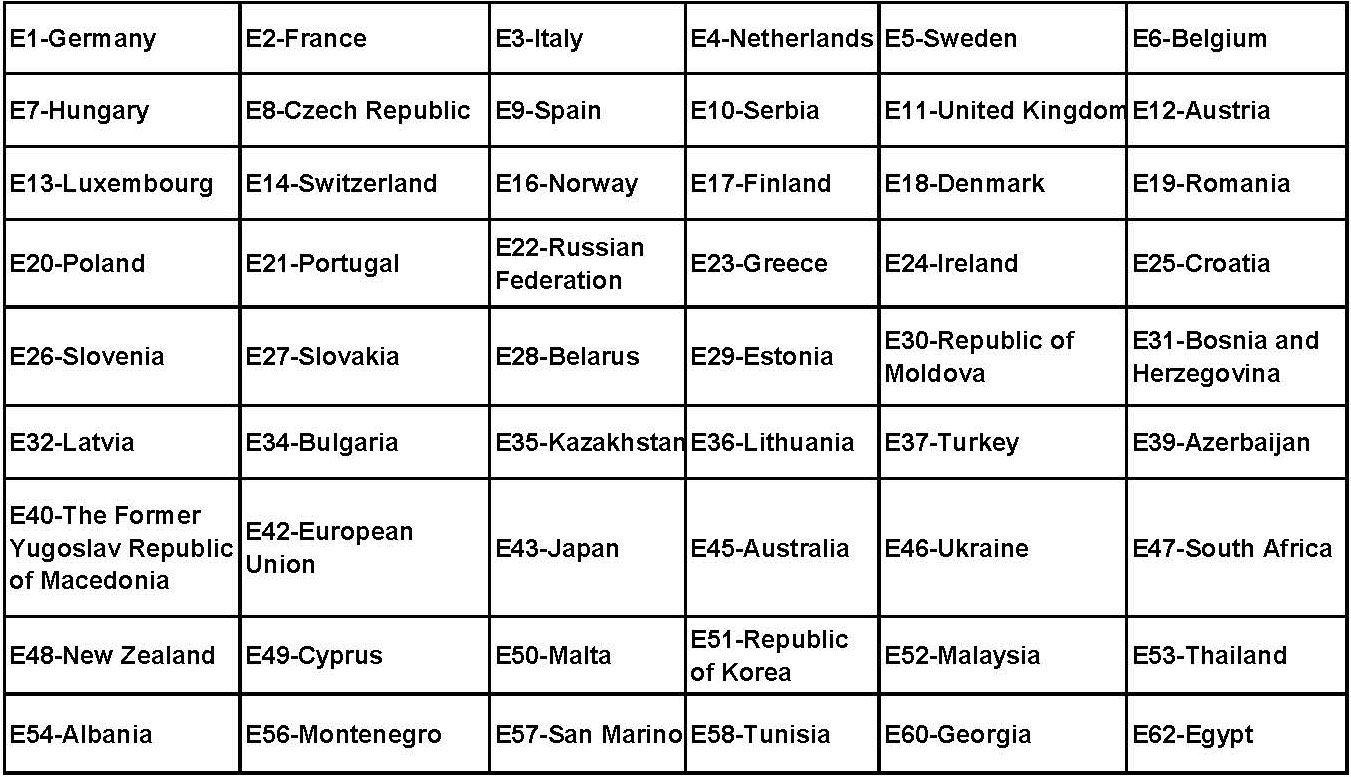
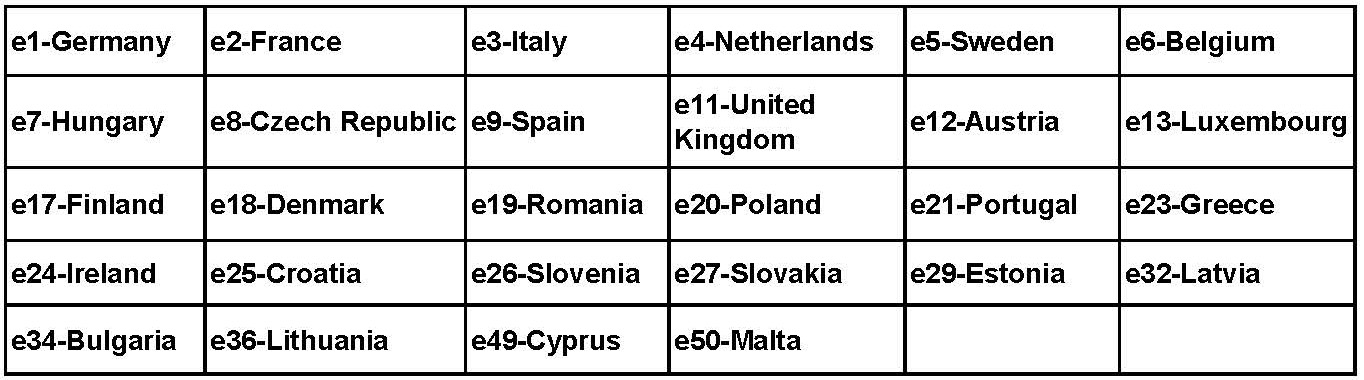
The e mark that approved by EEC is the certification mark of whole motor vehicle, safety component and system that theEuropean Union Commission compels the members countries to use according to EU directives. The testing organizations have to be the technical service organizations of EU members, the license issuing agencies are government transport agencies of EU members. The approved products which acquire the e mark will be accepted by all EU members. Different countries have their respective numbers:
The defference between E-mark and e-mark
|
Mark |
Exx |
exx |
|
specification |
(Regulation) |
(Directive) |
|
authority |
ECE |
EC |
|
head office |
Geneva |
Brussels |
|
membership |
all UN members |
need to be EC member countries |
|
applicable area |
Europe and other areas |
EC member countries |
|
Acceptability |
Non-mandatory, free choice |
Mandatory, must accept all provisions |
|
Whole vehicle certification |
No |
Yes |
E/e-Mark divides into two marks, one withrectangle frame, the other with circular frame, they represent different meanings.
|
|
Rectangle Frame:mean the products that can normal use but not have to when the vehicles in the stopped and running status. Such as vehicle-mounted charger, lamps/ flashlight, gas pump, massage /heating cushion, fan, electric kettle, fridge, coffee pot, TV/sound box, electric jack, dust collector,electric tool,etc. |
|
|
Circular Frame:mean the products wehave to use when the vehicles in the stopped and running status. Such as windshield, seat belt, head lamp, etc. |
|
The numbers in frames 1,2,…13…, each represents the EU country code that issues e-Mark certification. For example: No.1 representsGermany, No.4 represents Holland, No.11 represents England, No.23 represents Ireland, etc., that is the codes represent the corresponding countries’ e-Mark certifications issued by their departments of transportation. |
|
1、Whole vehicle E/e-mark approval
The definitions of EU vehicle classes and types
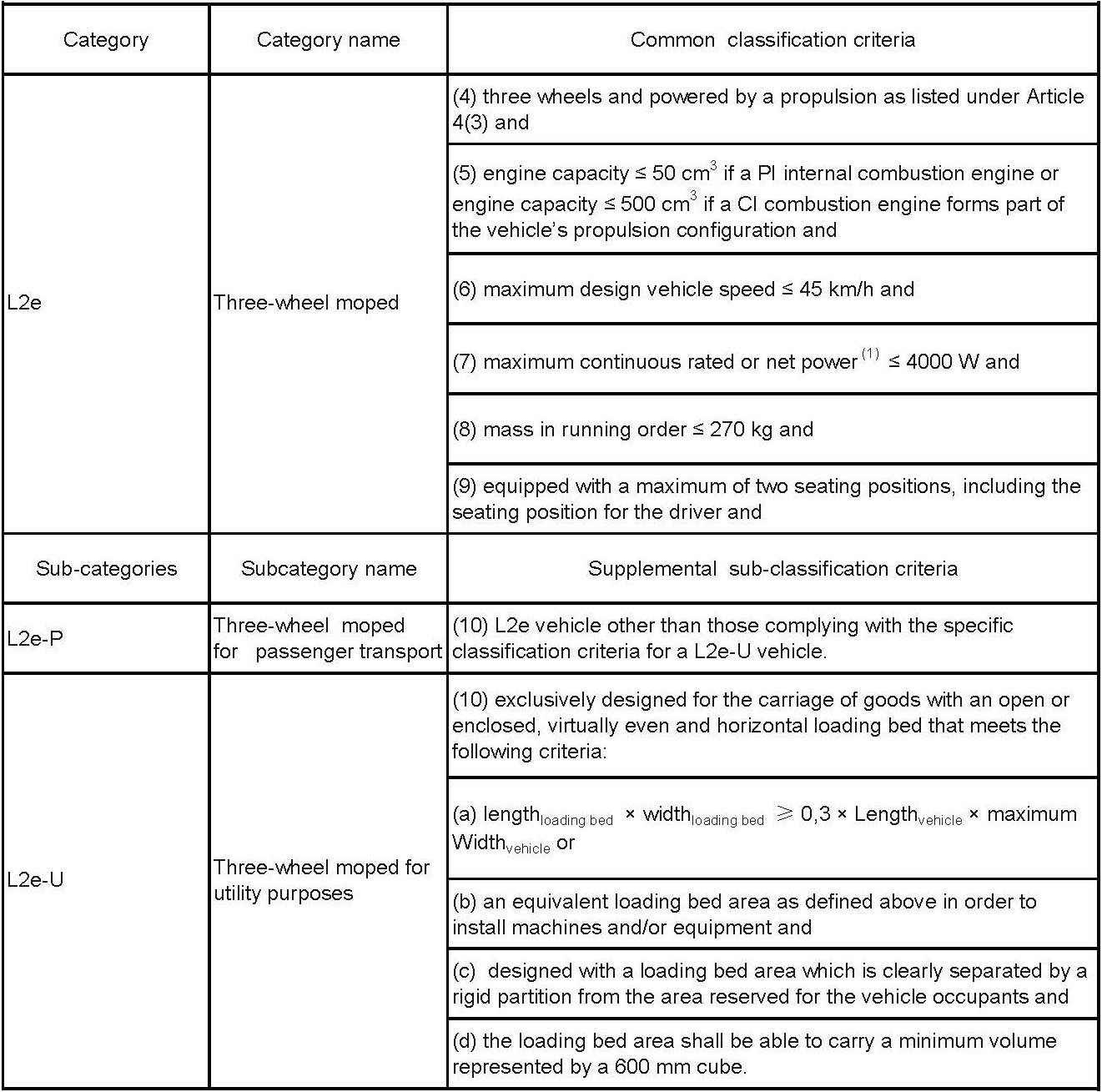
(1)Type M: the motor vehicles that at least have 4 wheels and used for carrying passengers.
Type M1: The passenger vehicle that the seats less than 8 including the driver's.
Type M2: The passenger vehicle that the seats more than 8 including the driver’s and maximum total mass is less than 5 tones.
Type M3: The passenger vehicle that the seats more than 8 including the driver’s and maximum total mass is more than 5 tones.
(2)Type N: The motor vehicles that at least have 4 wheels and used for carrying cargo.
Type N1: The cargo vehicles its maximum total mass is less than 3.5 tones.
Type N2: The cargo vehicles its maximum total mass is more than 3.5 tones but less than 12 tones.
Type N3: The cargo vehicles its maximum total mass is more than 12 tones.
The tractive vehicle designed for hooking up semitrailer or centre axle trailer, its vehicle weight that decides the vehicle types includes tractive vehicle’s weight in driving , the maximum vertical static load delivered by semitrailer or centre axle trailer, and maximum loading weight the tractive vehicle itself(if it has).
(3)Type O: trailer (involve the semitrailer)
Type O1: The trailer its maximum total mass is less than 0.75 tone.
Type O2: The trailer its maximum total mass is more than 0.75 tone but less than 3.5 tones.
Type O3: The trailer its maximum total mass is more than 3.5 tones but less than 10 tones.
Type O4: The trailer its maximum total mass is more than 10 tones.
As far as the semitrailer or centre axle trailer, the maximum total mass that decides the vehicle types is the static load that perpendiculars to ground when the semitrailer or centre axle trailer is full load and links together with the tractive vehicle.
Corrected vehicle type certification after the frame instruction(Reference(EC) No 2007-46)
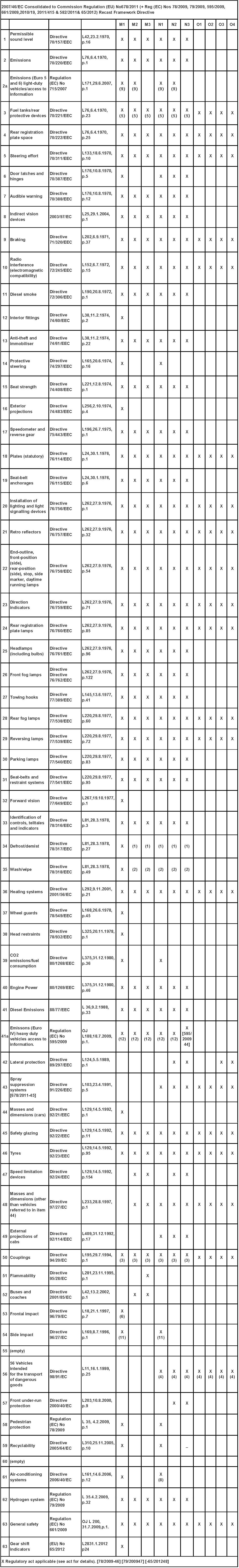
2、The whole motorcycle E/e-mark approval
Thedefinition of EU motorcycle types

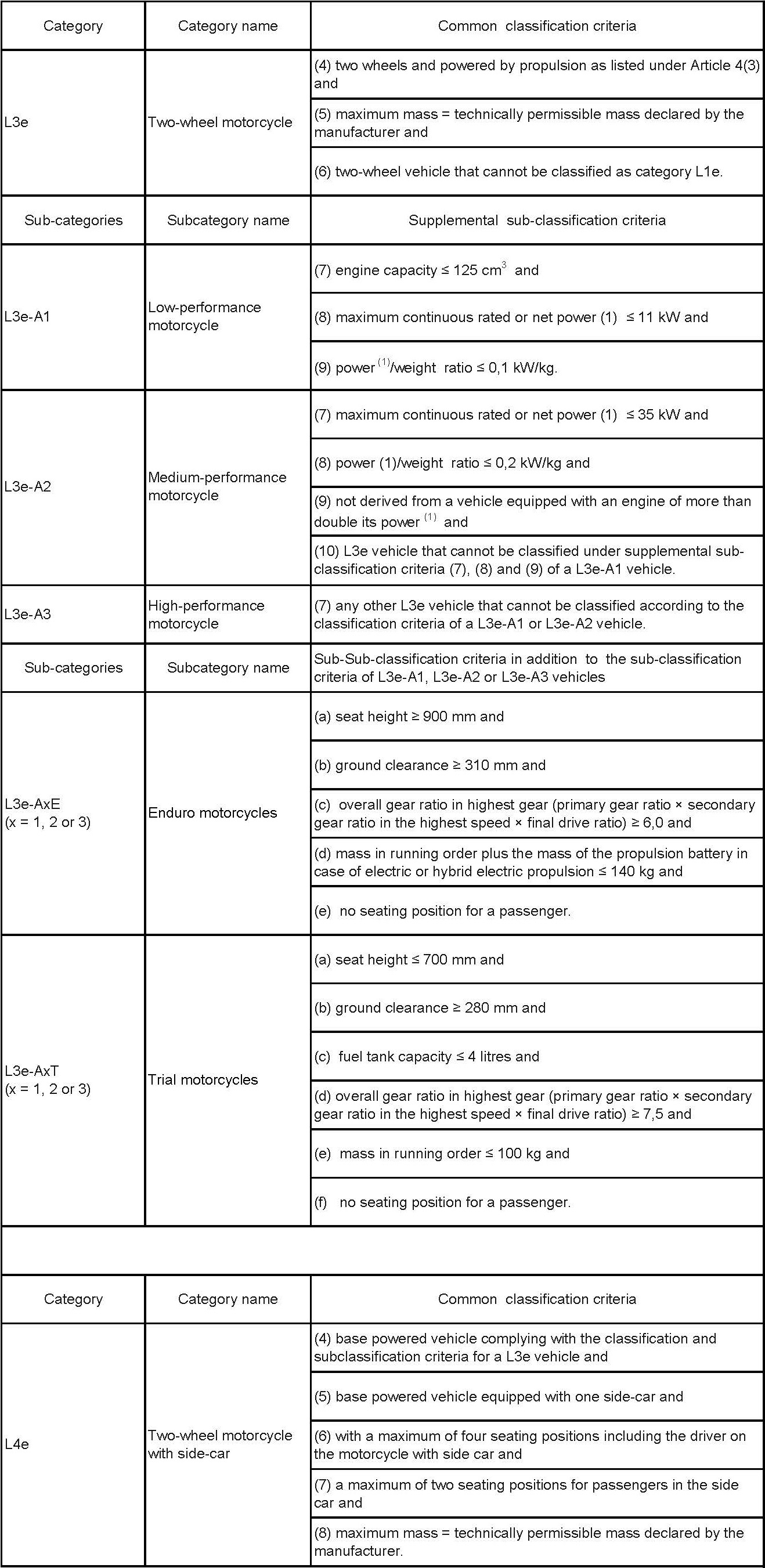

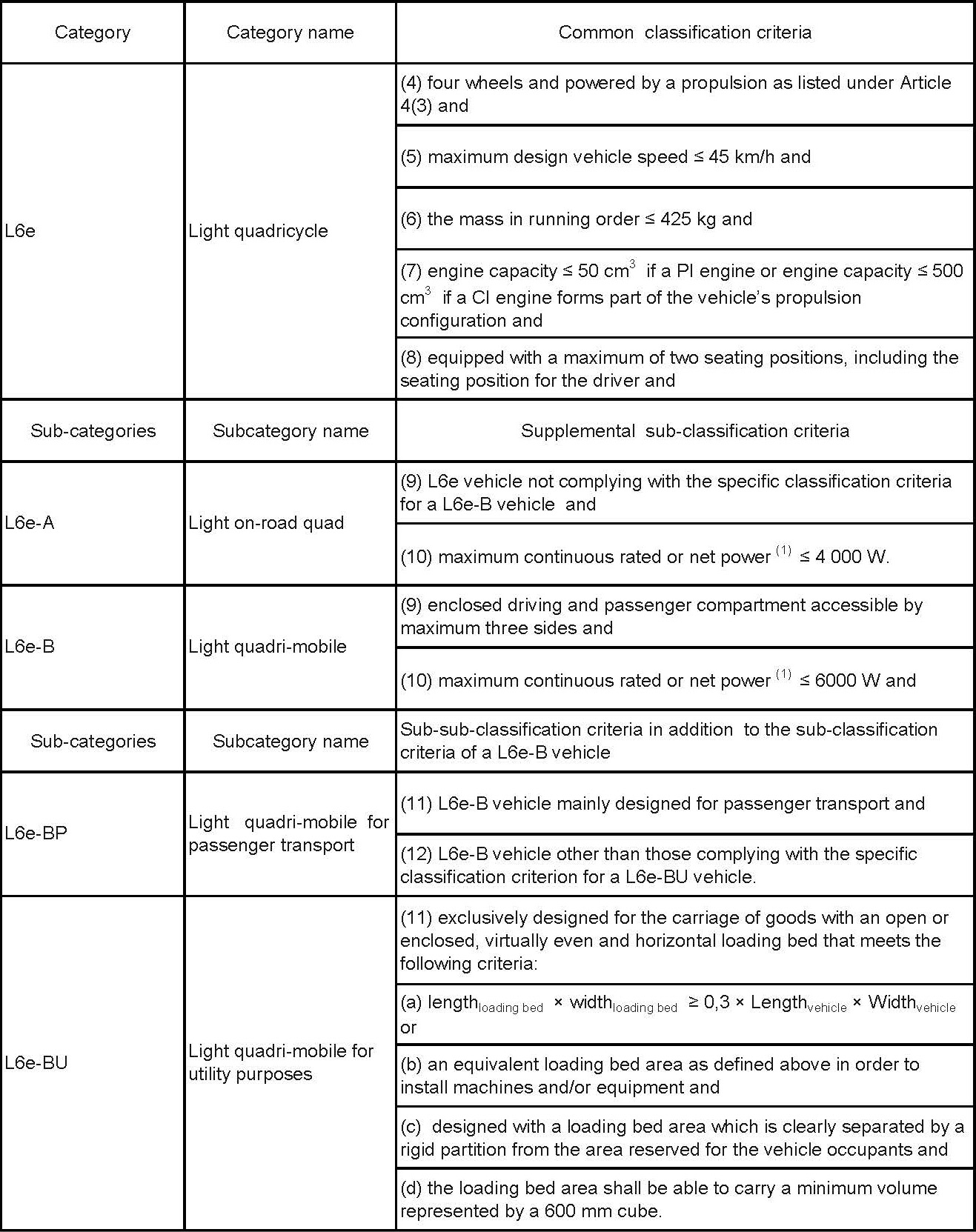
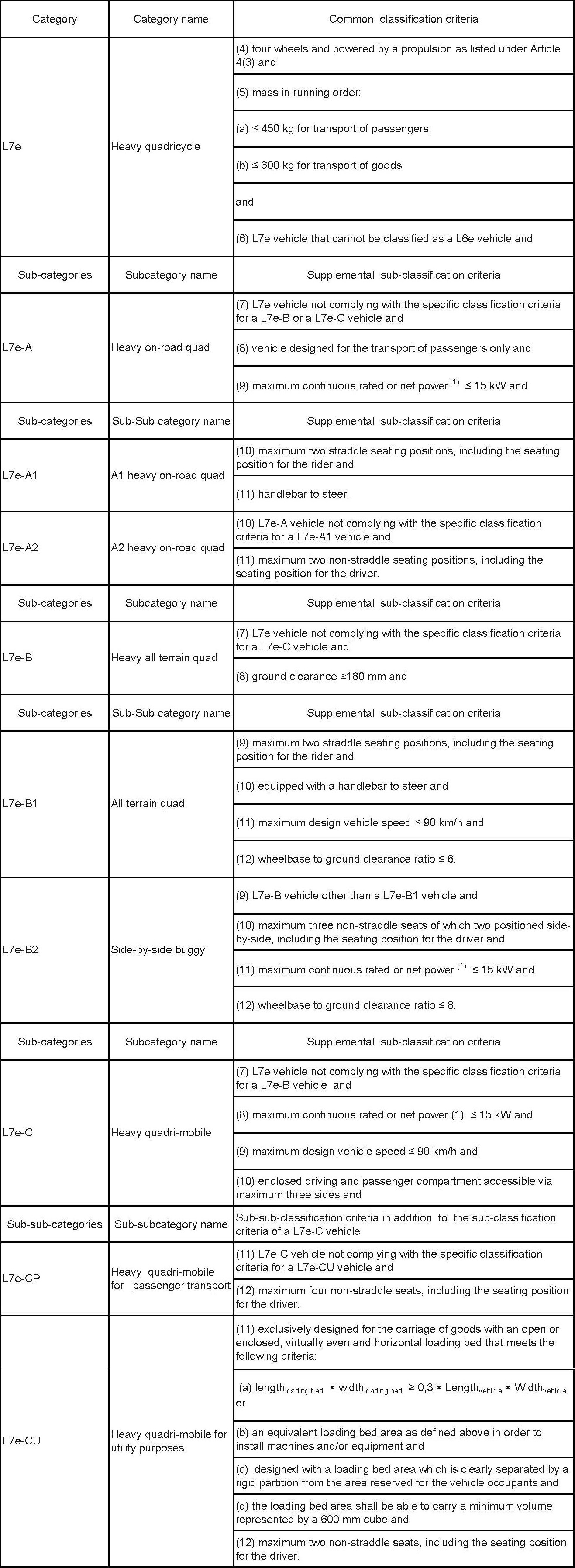
Items list of whole vehicle certification regulation
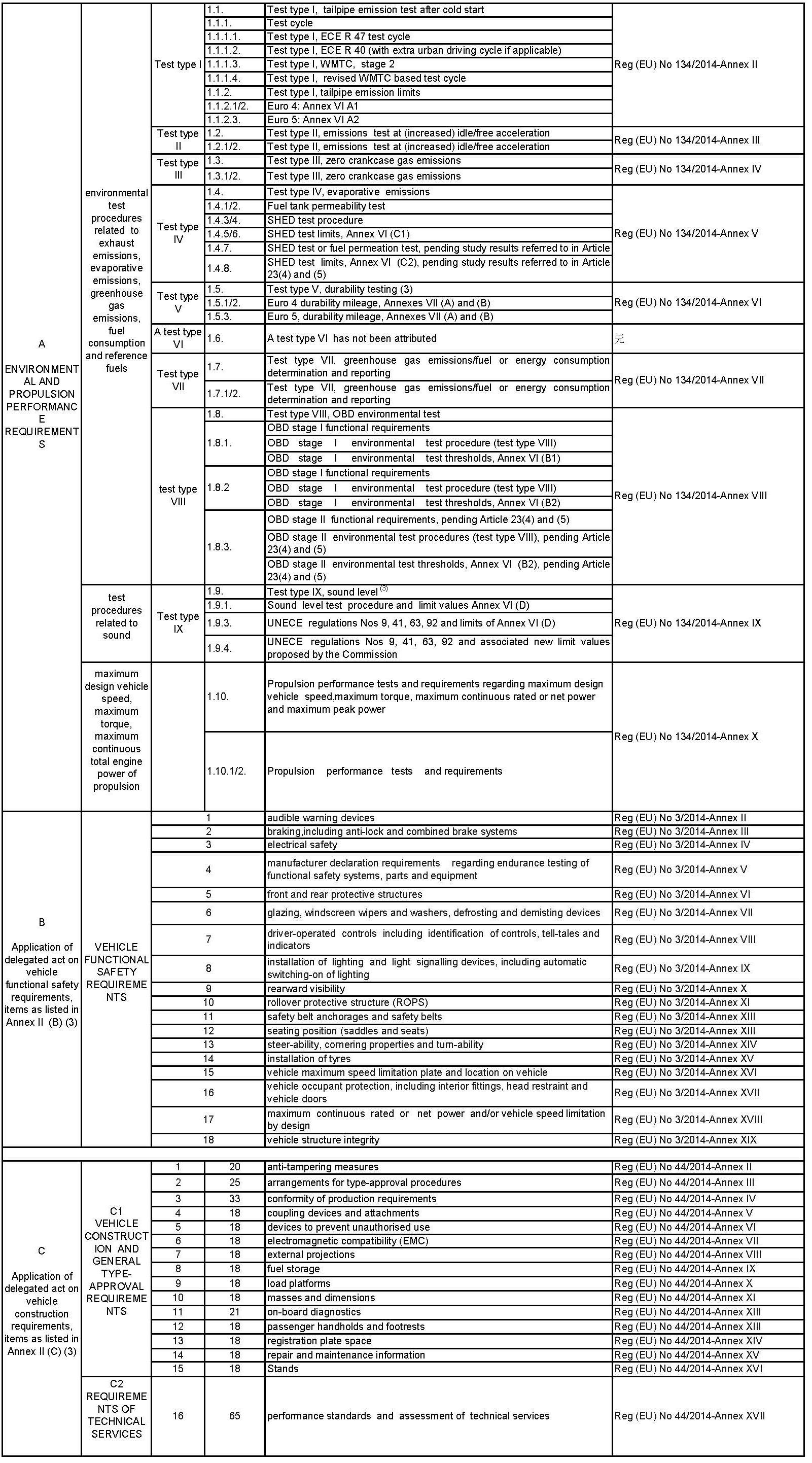
3、The tractor whole vehicle e-mark approval
Tractors (tractive vehicles) divide into the following categories
a:fo rwheeled tractors with a maximum designspeed below or equalto 40 km/h.
b:fo rwheeled tractors with a maximum designspeed above 40 km/h.
T1:wheeled tractor (tractive vehicle): the maximum design speed less than 40 km/h, at least one axle’s minimum wheel track less than 1150mm, unladen weight and driving weight exceed 600kg and ground clearance less than 1000mm.
T2:wheeled tractor (tractive vehicle): the maximum design speed less than 40 km/h, the minimum wheel trackmore than 1150mm, unladen weight and driving weight exceed 600kg and ground clearance less than 600mm. But when the average that each axle’s minimum wheel track divided by the height of gravitational center (relative to ground-based measurement) of tractor exceeds 0.90, the maximum design speed will be confined to 30 km/h.
T3:wheeled tractor (tractive vehicle): the maximum design speed less than 40 km/h, the unladen weight and driving weight less than 600kg.
T4:the tractor (tractive vehicle) which its maximum design speed less than 40 km/h.
T4.1 High-clearance tractors
The tractor (tractive vehicle) used at high growth cropland, such as liana. High chassis or sectional chassis are its features, used to load or operate the tools installed in the front, between the axles, rear-end or the load platform. When it’s in the working position, the vertical distance of ground clearance exceeds 1000mm. But when the average that all axles’ minimum wheel track divided by the height of gravitational center (relative to ground-based measurement, installing common tyres) of tractor exceeds 0.90, the maximum design speed will be confined to 30 km/h.
T4.2 Extra-wide tractors
The tractors (tractive vehicles) have large size mainly used on large areas of croplands.
T4.3 Low-clearance tractors
Four wheel drive farm or forestry tractors (tractive vehicles), the interchangeable farm or forestry equipment, with the features of braced frame, equipping with one or more output device, allowable load not exceed 10 tones, the ratio of load to maximum unladen weight in running status is more than 2.5. In addition, the center of gravity of the kind of tractors (tractive vehicles) is more than 850mm (relative to ground-based measurement, installing common tyres).
T5: the tractor (tractive vehicle) which its maximum design speed exceeds 40 km/h.
4、Vehicle lamps E/e-mark approval
E/e-mark certification and instruction orders list of vehicle lamps
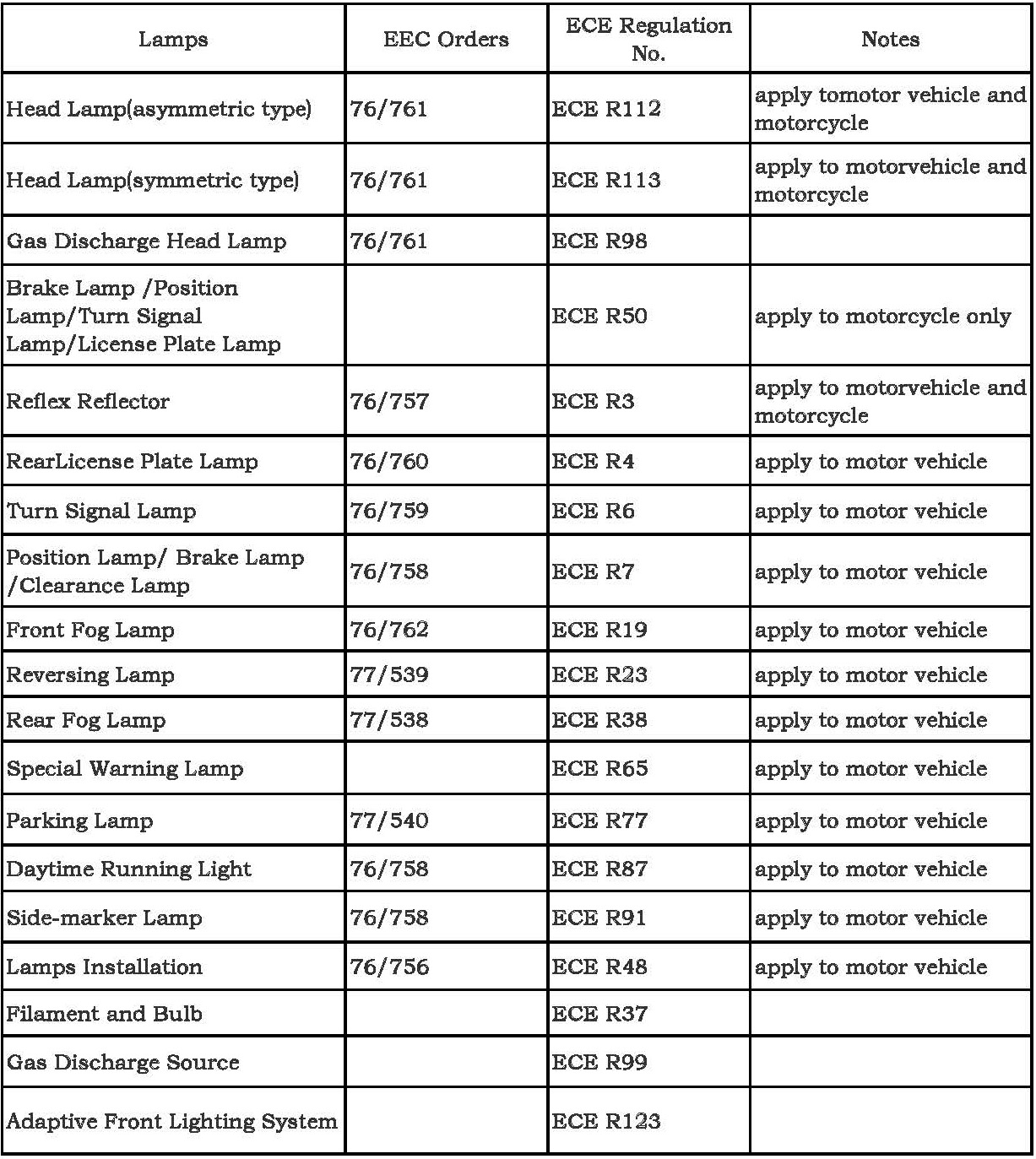
5、Vehicle components E/e-mark approval
vehicle components E/e-mark certification scope
Vehicle components: lamps, bulb, kinds of view mirror, tyre, rim, brake, horn, anti-theft device, seat belt, automotive glass, brake pad, exhaust pipe, etc.
Vehicle subsidiary accessories: safety helmet, child safety seat, subsidiary electrical products in car, etc.
From the October 2002 on, all vehicles, vehicle components and electronic products used in vehicle have to execute EMC test. The all electronic components sold in Europe have to agree to meet the ECE instruction 95/54/EC, the self-declaration according to EMC instruction 89/336/EEC will be not valid, and the vehicle products Notified Bodies that authorized by EU issue the E/e-Mark certificates. That is the CE(EMC)certification of vehicle electronic products and electronic components applied previously will be not valid anymore from October 2002 on, and the only way to access the European market is reapplying the E/e-Mark certificate issued by the Ministry of Communications of European countries.
vehicle components E/e-mark certification regulations and instructions
The E/e-Mark certification of motor vehicle components and system components need to test according to the corresponding regulations and instructions.
main vehicle components and corresponding regulations and instructions list

6、The Manufacturer Conformity of Production (COP) Audit Introduction
According to the relevant requirements of EU regulations of EEC/ECE, all manufacturers applying for EEC/ECE certification, whose products enter into the EU market, they have to receive the COP audit required by EU countries after passing the certification test.
Auditconcerns as follows:
File preparation
(1)ISO/TSQuality Management System. ISO9000/TS/QS Certificate.
(2)Quality Manual,Program File and ExecutionRecords.
(3)Control Plan and ExecutionRecords.
Main auditprojects
(1)System files audit (quality policy, quality control, quality assurance, quality improvement)
a) quality manual, quality objective, program file
b) audit reportmanagement
C) annualinternal audit report
(2)File Control
a) file control list
b) drawing files, external origin file, European rules control
c) document distribution, cancellation, recycle, destruction records
d) COC certificate management (whole vehicle factory)
(3)Record control
a) records list
b) quality records keep more than 5 years
(4)The control of projectalteration
a) informing certification agency and VCA to determine whether need test if the products alter.
b) clear introduction should be appeared in program file.
(5)Training
a)training plan
b)training records,performance evaluation records
c)inspector, operatortraining records,
(6) Production site
a) operationspecification
b) inspection specification
c) inspection record
d) equipment ledger, annualturnaround plan, daily spot check record
(7)Measuring instrumentsverification
a) measuring instruments ledger
b) verification plan
c) certificates
(8)Defectiveproducts control
a) supplied material, semi-finished product, defective products control
b) defective productsdistrict partition
c) concession reception rules
(9)Supplier Management
a) qualified suppliers list
b) suppliers classification and evaluation
(10)Customer satisfaction and internal audit management
(11)Warehouse
a) the raw materials warehouse, first in and first out, inspection specification, staff responsibility, goods stacking
b) finished stock storeroom, packing, logo print, with program files or work instructions
(12)Laboratory and experimental equipment, the experiments can’t be finished by manufacturers should sign the outsourcing agreement
(13)Control plan
Inaccordancewith the regulation required control plan (Englishedition), from material purchase to product packing finished. Including the experiment frequency.
Note: having the system operation records of at least three months